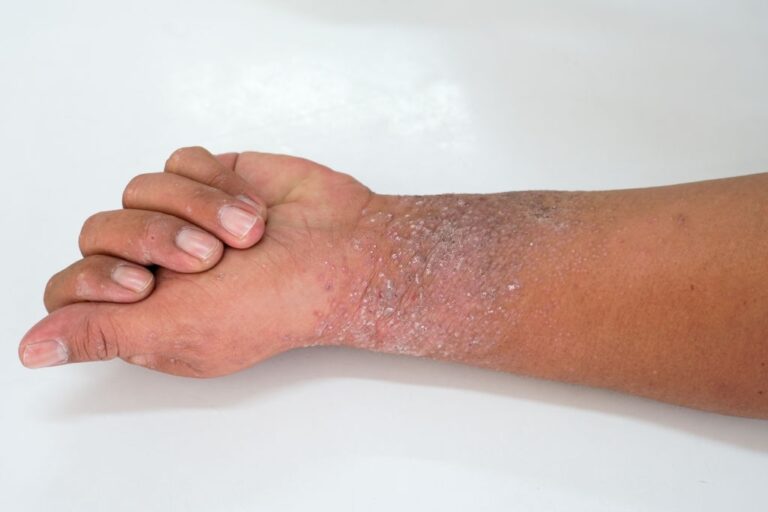
Eczema is a common skin condition that inflames the skin and makes it dry and itchy.
It affects people of all races and skin color, but it is a more likely to affect dark-skinned people more that people with other skin colors.
According to the National Eczema Association, African American children have the highest incidences of eczema at 20.2%, with Asian and native American children coming next at 13% each, white children at 12.1% and Hispanic children at 10.7%.
Black adults also suffer from eczema, and it occurs more in women.
Types of Eczema
Eczema is an umbrella term. There are many conditions that are general called eczema. They are:
- Atopic dermatitis (when inherited. Occurs with asthma and hay fever)
- Contact dermatitis
- Dyshidrotic eczema
- Nummular eczema
- Stasis dermatitis
Eczema could have a relapsing-remitting pattern. That means symptoms can shoe up and clear repeatedly. Triggers of eczema that follow a relapsing-remitting pattern include
- Allergies
- Extreme temperatures
- Dry or coarse skin
- Irritants
Symptoms of Eczema
The symptoms of eczema are dependent on the stage it is at. At the acute stage, there might be burning, itching and pain in the hands and trunks. It can cause irritated skins and bumps. Similar signs are exhibited at the subacute stage, often leading to
Dark-skinned people are prone to eczema, they also suffer severe cases.
Treating Eczema
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are commonly used to treat Eczema. Corticosteroids can be topical, oral or injected and the strength of the prescribed treatment is dependent on the location and severity of the eczema
Corticosteroids can have side effects such as unwanted hair growth, stretch marks and thinned skin.
Topical Immunomodulators
Topical Immunomodulators (tacrolimus and pimecrolimus) don’t have steroid, reducing the probability of side effects associated with Steroids. They are applied twice daily till the eczema clears.
The side effects of topical immunodilators are burning and itching.
Phototherapy (light treatment)
Phototherapy is an effective treatment. Different wavelengths of sunlight are administered to the patient’s skin twice weekly until the eczema clears.
It can result in sunburn and redness if precautions are not taken.
Antihistamines can be used to relieve itching.
Managing Eczema
During the course of treatment or before starting a treatment procedure, you have to modify your skin care habits and products.
First, avoid excess exposure to sun as perspiration could cause an eczema flare. Also, use mild, non-perfumed cleaners and ensure you stay in cool, well-ventilated areas.