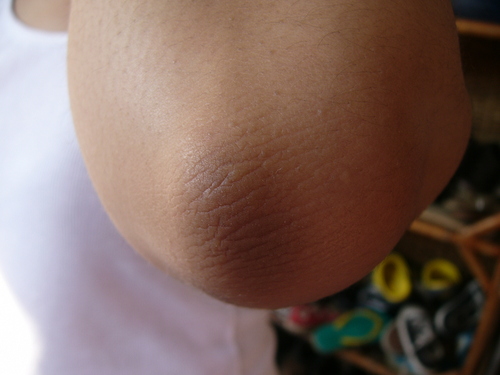
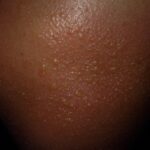
Hyperkeratosis is a defect that occurs particularly in women with rich complexion. Due to excess in keratin accumulation, the skin gradually thickens. Hyperkeratosis is often painless and shields the skin from pressure, excessive rubbing and irritation. While it may occur anywhere, there are certain areas more prone to hyperkeratosis. These areas include; the palms, soles, heels, elbows and knees.
The skin on the elbows and knees thickens as a result of frequent leaning, kneeling or pressure on the elbows and knees. In the same vein, the soles thicken due to consistent pressure which may arise from uncomfortable shoes or barefooted walking. Calluses which are a form of hyperkeratosis develop on the palms as a result of rough usage and pressure on them.
A unique form of hyperkeratosis, is keratosis pilaris. This occurs on the back of the arms, inside the knees and the front areas of the thighs. This is often characterized by rough tiny bumps around the hair follicle. It should be noted that these bumps are not caused by dirt, as is commonly believed. There is no clearly identified cause yet, but it (keratosis pilaris) is often associated with ichthyosis vulgaris, and at times eczema.
Ichthyosis is a special type of hyperkeratosis which can be passed down or inherited. It often appears scaly and dry, and comes in varying types – the commonest of which is the ichthyosis vulgaris.
A simple examination of your skin by a doctor would reveal if and what type of hyperkeratosis you’re dealing with. The diagnosis would help determine the appropriate treatment for you. Please note that certain types of hyperkeratosis have no cure, hence it is always best to prevent hyperkeratosis.
How to Prevent Hyperkeratosis
- For your elbows and knees, here are basic prevention tips;
- Avoid resting on your knees and elbows.
- Use a soft pad or platform when kneeling is necessary.
- Avoid rubbing or applying unnecessary pressure on your elbows and knees.
For your soles, here are tips to avoid calluses and corns;
- Wear shoes that evenly distribute your weight on both soles – low heels are a plus.
- Avoid tight shoes, high heels and stilettos.
- At all cost, stop walking barefooted.
- Avoid unnecessary pressure or scrubbing of your soles.
Get Treated!
Treating hyperkeratosis is dependent on the type, cause, severity and location of the hyperkeratosis. A vast number of treatments are geared towards softening and reducing the excess keratin. This is often achieved with the use of topical creams with active ingredients such as alpha-hydroxy acid (lactic or glycolic acid), salicylic acid, tretinoin or urea. For brown skinned women, hyperkeratosis often comes with skin discoloration, hence skin whitening creams are advised.
Salicylic acid which is a major ingredient against hyperkeratosis is a loosening agent that breaks up keratin, and this aids the softening of the skin. Salex Cream which contains salicylic acid, is a periodically released lotion that aids skin hydration by reducing the loss of water from the skin.
Topical creams with urea as an active ingredient help treat hyperkeratosis by ensuring skin hydration. Urea further breaks up keratin to soften the skin. Tretinoin boosts the shedding of thickened layers of skin, while acids such as the alpha-hydroxy acids, soften the skin by removing the accumulated keratin.
Conclusion
Hyperkeratosis of the skin is often annoying and seen as an embarrassment for women with rich complexion. No matter the affected area, topical creams that aid in removing thickened skin layers whilst softening the skin, are your best bet. Don’t get too carried away when rubbing these areas, as you’d only worsen the situation.