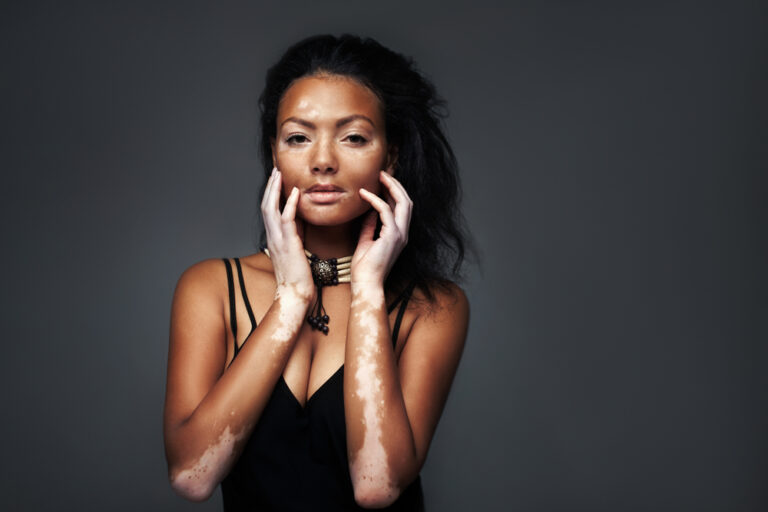
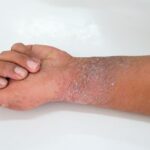
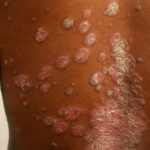
Vitiligo causes the appearance of white patches on the skin. It occurs when melanocytes (the cells producing melanin) are destroyed, leading to the appearance of white patches on the skin, lips, eyes, neck, genitals, places where skin folds, and in the hair.
Vitiligo is generally perceived to be hereditary, as most patients have a first-degree relative with vitiligo. It occurs before age 20 in more than half of the number of patients.
It affects about two percent of the population of the world. people have vitiligo across all races and genders, but it is often prominent among rich-complexions because of the contrasts in pigment.
Vitiligo is often distressing. Apart from the psychological trauma that might result from having vitiligo, patients often face negative remarks and isolation. In many cultures, vitiligo is viewed with negative connotations leading to discrimination and body shaming.
Types of vitiligo
Vitiligo is categorized based on where it is located and the pattern it assumes. There are five main types namely focal, generalized, acrofacial, segmental, and universal.
- Focal vitiligo: causes few white patches on the skin. Minimal effects.
- Generalized vitiligo: causes symmetrical patterns on the skin.
- Acrofacial vitiligo: Occurs around the hands, eyes, and mouth. Often white.
- Segmental vitiligo: Linear white patches.
- Universal vitiligo: Covers almost all parts of the body.
Treating Vitiligo
Vitiligo is difficult to treat. Also, treatments might not clear it completely. A combination of treatments however increases the chances of success when treating vitiligo.
A person might consider one or more of these treatments
Camouflaging
Cosmetics can be used to conceal affected parts of the skin. You can consult a professional to help you choose products that match your skin color and to teach you how to apply them.
Topical Creams
Topical creams can be effective in the treatment of localized vitiligo. The uses of corticosteroids and tacrolimus(topical) when taken for about four months.
Steroids can also be injected to treat vitiligo as well, though caution should be taken as it could thin the skin and accelerate the growth of blood vessels.
Phototherapy ( Ultraviolet Light)
Ultraviolet Light, though slow, can be used in the treatment of vitiligo. When combined with psoralen, it stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin. Pigment starts becoming visible gradually till it covers the skin. Melanocyte can be transferred from one part of the skin to another too.
Surgery
Mini grafts or suction-blister grafts of skin taken from normal patches are used to cover vitiliginous areas. It can take about 4 to 6 months.
Protection from the Sun
Sun burn is a risk for a person who has vitiligo; the affected patches cannot produce melanin to act as a shield against the harshness of sun rays. Sunbeds must be avoided and sunscreen must be used. Applying sunscreen protects the skin from sunburn and other damages