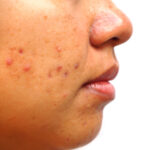
Acne is a skin condition that occurs when your hair follicles become congested with sebum (oil) and dead skin cells. It causes whiteheads, blackheads, papules or pustules. It can appear anywhere on the face or body, or specific regions (depending on the cause). It is most common among teenagers, though it can affect people of all ages at different stages.
Physical acne signs vary depending on the severity of your condition. This includes; whiteheads- which are white closed plugged pores. Blackheads- which are black open plugged pores. Papules- which are red small tender bumps. Pustules- which are red and large with pus at their tips. Nodules- which are solid large painful lumps under the skin. Cystic Lesions- which are painful pus-filled lumps under the skin. Also, the usual pigmentation issues, irritation, inflammation and scarring.
Acne forms in four stages
- overactive sebaceous glands: which can produce excess sebum, which is often thicker and stickier and has a tendency to lead to follicle congestion and an oily T-zone.
- Accumulation of dead skin cells: the skin naturally sheds dead skin cells but when you add excess sebum to the mix, they stick together and form an impaction plug, enabling breakout-causing bacteria to thrive.
- P. acnes: this bacteria is naturally present in our skin’s microbiome. When these are trapped in the skin without air, they feed on sebum and produce waste products causing visible breakouts that appear as comedones.
- Inflammation: When the skin becomes inflamed, they appear as red, swollen, and sometimes pus-filled breakouts- which can form into papules, pustules and cysts.